As we delve into the fascinating world of graph evaluation, it turns into obvious that the assertion ‘which assertion greatest describes the operate represented by the graph’ is a elementary cornerstone of understanding graph performance. A graph can symbolize a variety of capabilities, from linear to nonlinear, and every sort has its distinctive traits that decide the operate’s conduct. The presence or absence of intercepts and asymptotes, together with the continuity and Intermediate Worth Theorem, all play essential roles in graph evaluation.
The important thing to deciphering a graph lies in recognizing its options, together with axis labels and coordinates, which offer insights into the area and vary of the operate. Graph evaluation can also be influenced by the kind of operate represented, equivalent to linear, quadratic, or exponential, every with its distinct properties and conduct.
Understanding Graph Performance
Graphical illustration is a strong device for visualizing capabilities and its numerous traits. The graph of a operate offers priceless details about its conduct, serving to us to know how the operate’s output modifications because the enter or impartial variable modifications. By analyzing the graph, we will determine key options that decide the operate’s conduct, equivalent to its area, vary, intercepts, and asymptotes.
Traits of a Operate Represented by a Graph
A operate represented by a graph is usually depicted as a curve or floor on a coordinate airplane. The graph’s form and orientation convey details about the operate’s conduct, together with its rising, reducing, or staying fixed conduct. The graph additionally signifies the operate’s area and vary, that are the units of enter and output values the operate accepts. Key traits of a operate’s graph embrace its:
- Area: The set of enter values (x-coordinates) for which the operate is outlined.
- Vary: The set of output values (y-coordinates) produced by the operate for its area.
- Rising and reducing conduct: The course and fee at which the operate’s output modifications because the enter varies.
These traits of a operate’s graph present priceless insights into the operate’s conduct, serving to us to know the way it responds to modifications in its enter.
Key Options of the Graph that Decide the Operate’s Conduct
The graph of a operate is influenced by a number of key options that decide its conduct. These options embrace:
- Intercepts: The factors the place the graph intersects the x-axis and y-axis, which correspond to the operate’s x-intercepts and y-intercepts.
- Asymptotes: Traces or curves that the graph approaches because it goes to infinity or adverse infinity.
- Continuity: The diploma to which the graph is easy and unbroken, representing the continuity of the operate.
These options play an important function in figuring out the operate’s conduct and might help us to foretell the way it will reply to completely different inputs or situations.
The Significance of Intercepts and Asymptotes in Graph Evaluation
Intercepts and asymptotes are important options of a operate’s graph that present priceless insights into its conduct. Intercepts point out the factors the place the operate crosses the x-axis or y-axis, which may reveal details about the operate’s area and vary. Asymptotes, then again, symbolize the conduct of the operate because it approaches infinity or adverse infinity. By analyzing intercepts and asymptotes, we will acquire a deeper understanding of the operate’s conduct and make predictions about its response to completely different inputs.
The Position of Continuity and the Intermediate Worth Theorem
Continuity is a crucial facet of a operate’s graph, representing the diploma to which it’s easy and unbroken. A operate is steady if its graph could be drawn with out lifting its pen from the paper, which means that the operate’s values change easily and predictably because the enter modifications. The Intermediate Worth Theorem (IVT) states that if a operate is steady on a closed interval, it assumes all values between the operate’s values on the interval’s endpoints. This theorem has far-reaching implications for graph evaluation, enabling us to make predictions a few operate’s conduct and determine its key options.
“A operate is steady at a degree if its graph could be drawn with out lifting its pen from the paper.”
This profound perception into the character of continuity highlights the importance of the Intermediate Worth Theorem in graph evaluation, permitting us to extract priceless details about a operate’s conduct and predictions about its response to completely different inputs.
Graph Options and Operate Description
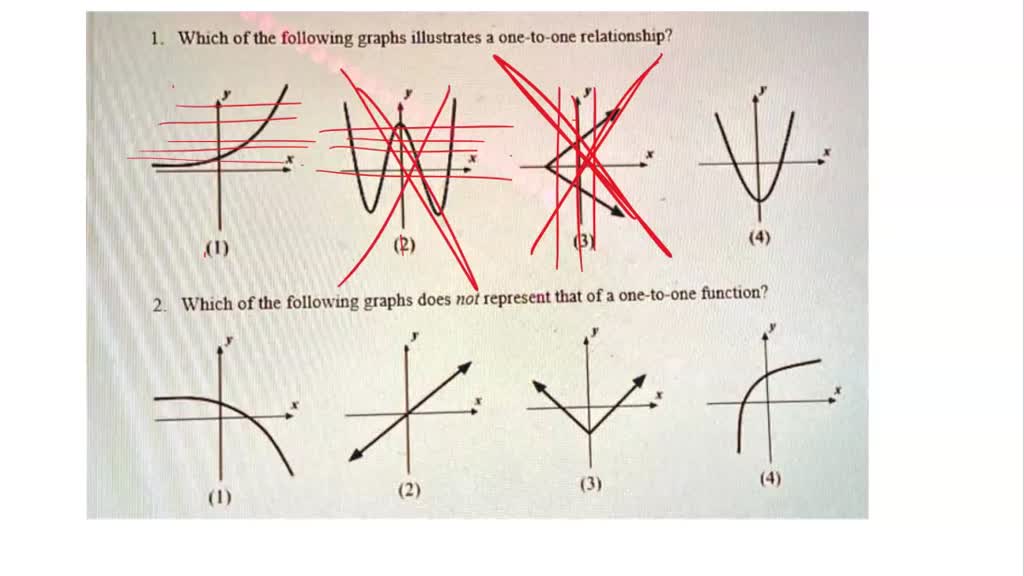
The graph represents a visible illustration of a operate, which might help us perceive the relationships between variables. It’s important to research the graph to interpret the operate’s conduct and determine its key options.
Kinds of Capabilities Represented by Graphs
A operate’s graph could be labeled into a number of sorts, every with its distinctive traits. The primary sorts of capabilities represented by graphs are linear, quadratic, and exponential.
* Linear Operate: A linear operate has a graph within the type of a straight line. The equation of a linear operate is usually within the type y = mx + b, the place m represents the slope and b represents the intercept. Examples of linear capabilities embrace y = 2x + 1 and y = -3x + 4.
* Quadratic Operate: A quadratic operate has a graph within the type of a parabola. The equation of a quadratic operate is usually within the type y = ax^2 + bx + c, the place a, b, and c are constants. Examples of quadratic capabilities embrace y = x^2 – 4x + 4 and y = x^2 + 2x – 3.
* Exponential Operate: An exponential operate has a graph within the type of a curved line that rises or falls quickly. The equation of an exponential operate is usually within the type y = ab^x, the place a and b are constants. Examples of exponential capabilities embrace y = 2^x and y = 3^-x.
Decoding Axis Labels and Coordinates
To grasp a operate’s graph, we have to interpret the axis labels and coordinates. The x-axis represents the enter or impartial variable, whereas the y-axis represents the output or dependent variable. Coordinates on the graph symbolize particular factors on the operate, and so they might help us determine the operate’s key options.
The area of a operate is the set of all doable enter values, whereas the vary is the set of all doable output values. Understanding the area and vary of a operate is essential to deciphering its graph and figuring out its key options. For instance, the area of the operate y = 1/x is all actual numbers besides 0, whereas the vary is all actual numbers besides 0.
Graph Options and Operate Properties
Graph options equivalent to maxima, minima, and inflection factors can affect a operate’s properties.
* A most is the best level on a operate’s graph, and it represents the best worth of the operate.
* A minimal is the bottom level on a operate’s graph, and it represents the least worth of the operate.
* An inflection level is a degree on a operate’s graph the place the curvature modifications.
We will discover the utmost, minimal, and inflection factors on a operate’s graph utilizing numerous methods, equivalent to discovering the spinoff or utilizing graphing software program. Understanding these options might help us make knowledgeable choices in real-world purposes.
Operate Varieties and Graph Traits: Which Assertion Greatest Describes The Operate Represented By The Graph
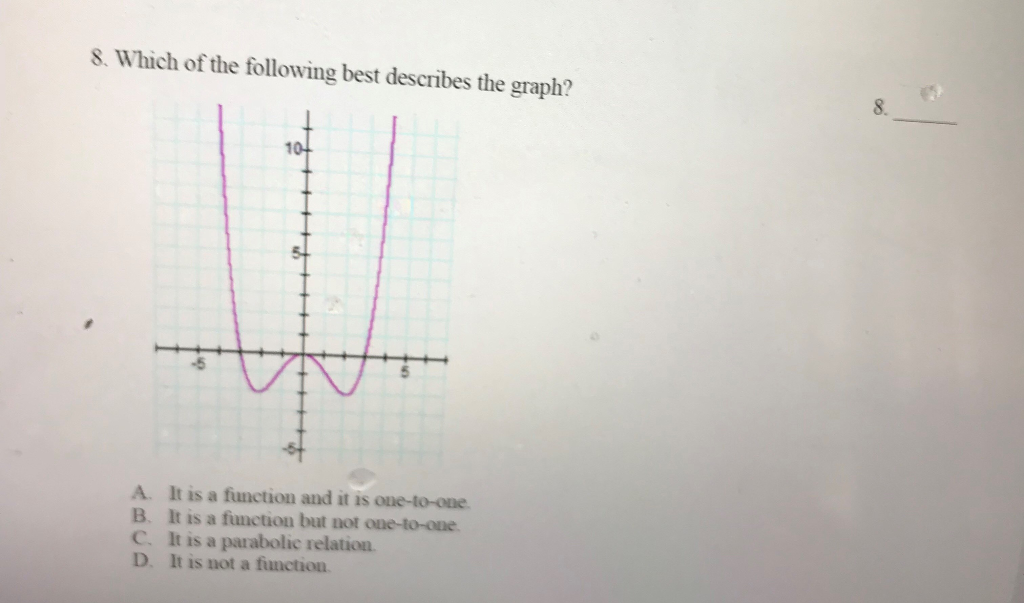
In arithmetic, capabilities and their graphs are elementary ideas that assist us perceive relationships between variables and predict real-world phenomena. Graphs of capabilities could be categorized into differing types primarily based on their traits, together with linearity, nonlinearity, rationality, and quadratic properties. By understanding these traits, we will higher analyze and interpret the conduct of capabilities in numerous contexts.
Graphical Illustration of Capabilities
A graph is a visible illustration of a operate, exhibiting the enter values (x-axis) and output values (y-axis) of the operate. The form, orientation, and place of the graph reveal essential details about the operate’s conduct, equivalent to its area, vary, and fee of change.
Linear and Nonlinear Capabilities
Linear capabilities have a continuing fee of change, leading to a straight line graph. Nonlinear capabilities, then again, exhibit a non-constant fee of change, resulting in curved or irregular graph shapes.
- Linear Capabilities:
- F(x) = 2x + 3: a linear operate with a slope of two and y-intercept of three.
- F(x) = x – 2: a linear operate with a slope of 1 and y-intercept of -2.
- Nonlinear Capabilities:
- F(x) = x^2 + 1: a quadratic operate with a parabolic graph form.
- F(x) = sin(x): a trigonometric operate with a periodic and oscillatory graph form.
Rational Capabilities
Rational capabilities have a numerator and denominator, leading to a graph with vertical asymptotes, horizontal asymptotes, or a mixture of each.
F(x) = (2x + 1) / (x – 1): a rational operate with vertical asymptote at x = 1 and horizontal asymptote at y = 2.
Quadratic Capabilities
Quadratic capabilities have a graph that may be a parabola, with a attribute “U” form. They are often categorized into differing types primarily based on their main coefficient and vertex.
- Quadratic Capabilities with Optimistic Main Coefficient:
- F(x) = x^2 – 4x + 4: a quadratic operate with a parabolic graph form and a vertex at x = 2.
- Quadratic Capabilities with Adverse Main Coefficient:
- F(x) = -x^2 + 2x – 1: a quadratic operate with a parabolic graph form and a vertex at x = 1.
Comparability of Linear and Quadratic Capabilities
| | Linear Capabilities | Quadratic Capabilities |
| — | — | — |
| | F(x) = mx + b | F(x) = ax^2 + bx + c |
| Area | (-∞, ∞) | (-∞, ∞) |
| Vary | (-∞, ∞) | (-∞, ∞) |
| Charge of Change | fixed | non-constant |
| Graph | straight line | parabola |
Actual-World Purposes of Graph Performance
In right now’s fast-paced world, knowledge is king, and graph performance is the crown that permits us to unlock its secrets and techniques. From optimizing logistics to predicting inventory market developments, graph evaluation performs an important function in numerous industries. On this part, we’ll dive into the real-world purposes of graph performance and discover its affect on our each day lives.
Optimization Issues in Numerous Fields
Graph evaluation is a strong device for fixing optimization issues in numerous fields, together with economics and engineering. By representing advanced methods as graphs, we will determine essentially the most environment friendly paths, optimize useful resource allocation, and cut back prices.
-
Examples of optimization issues embrace:
- Logistics optimization: Graph evaluation helps route supply vehicles and drivers to reduce journey time and gasoline consumption.
- Provide chain optimization: Graph evaluation optimizes the circulation of products and supplies, decreasing lead occasions and enhancing stock administration.
- Community optimization: Graph evaluation identifies essentially the most environment friendly routes for web site visitors, decreasing latency and enhancing total community efficiency.
Position of Graph Evaluation in Scientific Analysis and Knowledge Interpretation
Graph evaluation performs an important function in scientific analysis and knowledge interpretation. By analyzing advanced knowledge units, researchers can determine patterns and relationships that inform new discoveries and breakthroughs. Graph evaluation is utilized in numerous scientific fields, together with:
-
Examples of scientific purposes embrace:
- Genomics: Graph evaluation helps researchers determine genetic variations and predict illness susceptibility.
- Cosmology: Graph evaluation helps scientists mannequin the universe’s construction and evolution.
- Local weather modeling: Graph evaluation helps researchers predict and perceive local weather patterns.
Graph Transformation in Actual-World Eventualities
Graph transformation is a crucial facet of graph performance, enabling us to adapt and reply to altering conditions. In the actual world, graph transformation is utilized in numerous purposes, together with:
-
Examples of graph transformation embrace:
- Routing algorithms: Graph transformation helps adapt routing algorithms to altering site visitors patterns and highway circumstances.
- Suggestion methods: Graph transformation permits advice methods to adapt to consumer conduct and preferences.
- Fraud detection: Graph transformation helps determine and stop fraudulent exercise in monetary transactions.
Significance of Graph Evaluation in Finance and Financial Modeling
Graph evaluation is important in finance and financial modeling, enabling us to know and predict market developments and conduct. By analyzing advanced monetary knowledge units, graph evaluation helps:
-
Examples of economic purposes embrace:
- Predicting inventory costs: Graph evaluation helps determine patterns and developments in inventory costs.
- Portfolio optimization: Graph evaluation optimizes funding portfolios to scale back danger and maximize returns.
- Figuring out market developments: Graph evaluation helps determine rising developments and alternatives.
Graph evaluation is a strong device for unlocking insights and making data-driven choices. By embracing graph performance, we will drive innovation and resolve advanced issues in numerous fields.
Graph Illustration and Visualization
Graph illustration and visualization play an important function in speaking advanced knowledge insights successfully. It includes utilizing numerous strategies to translate uncooked knowledge into visible representations that facilitate understanding, interpretation, and decision-making. With the abundance of knowledge accessible, graph visualization has develop into an indispensable device for professionals, researchers, and lovers alike.
METHODS OF GRAPH VISUALIZATION
There are quite a few strategies of graph visualization, together with plots and charts, every suited to convey particular sorts of knowledge insights. Among the commonest strategies embrace:
- Plots: Scatter plots, line plots, and bar plots are examples of plots used to visualise relationships between variables or developments over time.
- Charts: Bar charts, pie charts, and histograms are sorts of charts used to check categorical knowledge or show distributions.
CHOOSE THE RIGHT GRAPH TYPE
Selecting the best graph sort for a given dataset is essential for efficient knowledge communication. Totally different graph sorts are suited to numerous knowledge traits, such because the variety of variables, knowledge distribution, and supposed viewers. As an illustration:
- A scatter plot is appropriate for visualizing relationships between two steady variables.
- A bar chart is good for evaluating categorical knowledge throughout a number of teams.
CREATING A GRAPH REPRESENTATION
Making a graph illustration of a real-world state of affairs includes a number of steps:
- Outline the analysis query or drawback to be addressed.
- Accumulate and put together related knowledge.
- Choose an acceptable graph sort primarily based on the info traits.
- Design and customise the graph to enhance communication and readability.
- Interpret and draw conclusions from the graph insights.
EXAMPLES OF GRAPH TYPES, Which assertion greatest describes the operate represented by the graph
Some widespread graph sorts embrace:
| Graph Kind | Description |
|---|---|
| Bar Chart | Used to check categorical knowledge throughout a number of teams. |
| Scatter Plot | Used to visualise relationships between two steady variables. |
| Line Graph | Used to show developments over time or to check completely different classes. |
Last Ideas
By graph evaluation, we acquire a deeper understanding of the relationships between variables and the conduct of capabilities, which has far-reaching implications in numerous fields, together with economics, engineering, scientific analysis, and finance. By mastering the artwork of graph evaluation, we will unlock new insights and options to advanced issues, making it a vital device in right now’s data-driven world.
Person Queries
What’s the significance of graph evaluation in real-world purposes?
Graph evaluation has vital implications in numerous fields, together with economics, engineering, scientific analysis, and finance, the place it helps resolve optimization issues and unlock new insights.
How do intercepts and asymptotes affect graph conduct?
Intercepts and asymptotes play essential roles in figuring out the conduct of graphs, with intercepts indicating factors the place the operate crosses the axis and asymptotes exhibiting horizontal or vertical strains that the operate approaches as x or y values develop into massive.
Are you able to present an instance of graph transformation in real-world situations?
Sure, graph transformation has many real-world purposes, equivalent to adjusting manufacturing ranges in response to market developments or optimizing useful resource allocation to maximise effectivity.
How does graph evaluation affect finance and financial modeling?
Graph evaluation has a big affect on finance and financial modeling by permitting researchers to mannequin and predict advanced financial methods, making knowledgeable choices and optimizing useful resource allocation.
Can graph evaluation be used to optimize issues in different fields?
Sure, graph evaluation has far-reaching implications in numerous fields, together with engineering, scientific analysis, and drugs, the place it helps resolve optimization issues and unlock new insights.