What are one of the best methods to forestall a sampling error – When conducting analysis, some of the essential components to contemplate is the potential for sampling error, which may considerably impression the accuracy of outcomes. By understanding the significance of sampling error and implementing efficient methods to forestall it, researchers can be certain that their findings are dependable and significant. On this overview, we’ll discover one of the best methods to forestall sampling error and enhance the standard of analysis outcomes.
Sampling error happens when there’s a distinction between the pattern information and the inhabitants information, which may occur on account of numerous causes similar to biased sampling, information assortment errors, or under- or over-sampling. To forestall sampling error, researchers want to pick a consultant pattern inhabitants, use applicable information assortment strategies, and analyze information accurately.
Understanding Sampling Error
Understanding sampling error is essential for researchers, information analysts, and anybody who depends on statistics to tell their selections. Sampling error happens when a pattern of a inhabitants is used to make inferences about the entire inhabitants, and the outcomes are topic to error on account of numerous components. On this part, we are going to delve into the definition of sampling error, its impression on analysis outcomes, and the distinction between sampling error and non-sampling error.
Definition and Influence of Sampling Error
Sampling error is the distinction between the pattern statistic and the corresponding inhabitants parameter. It happens when the pattern doesn’t precisely signify the inhabitants, resulting in biased or inaccurate outcomes. The impression of sampling error may be important, affecting the validity and reliability of analysis findings. For example, if a pattern is biased in the direction of a selected demographic, the outcomes will not be generalizable to the bigger inhabitants.
Distinction between Sampling Error and Non-Sampling Error
There are two varieties of errors that may happen in analysis: sampling error and non-sampling error. Sampling error is because of the pattern not precisely representing the inhabitants, whereas non-sampling error is because of flaws within the measurement course of or information assortment strategies. Non-sampling errors can embrace errors on account of human bias, measurement errors, or information entry errors. For instance, if a survey query is worded in a manner that results in biased responses, non-sampling error would happen, whereas if the survey is performed on a small, unrepresentative pattern, sampling error would happen.
Examples of Sampling Error
Sampling error can happen in numerous conditions, similar to:
- Involuntary self-selection bias: When contributors self-select right into a examine, they could not precisely signify the inhabitants, resulting in biased outcomes. For instance, if a examine on smoking cessation is performed on a pattern of wholesome people, the outcomes will not be generalizable to people who smoke with persistent well being situations.
- Mechanical sampling error: When the pattern is collected utilizing a mechanical course of, similar to random digit dialing, sampling error can happen if the pattern isn’t consultant of the inhabitants. For example, if a pattern is collected from a particular time-frame, it might not precisely signify the inhabitants’s opinions or behaviors.
- Voluntary response bias: When contributors voluntarily reply to a survey, they could not precisely signify the inhabitants, resulting in biased outcomes. For instance, if a survey on buyer satisfaction is performed on a pattern of enthusiastic prospects, the outcomes will not be generalizable to dissatisfied prospects.
Sampling error may be minimized through the use of consultant samples, making certain correct information assortment and measurement, and accounting for potential biases. By understanding the idea of sampling error and its impression on analysis outcomes, researchers and information analysts could make knowledgeable selections and enhance the validity and reliability of their findings.
Designing an Correct Pattern

When conducting a survey or accumulating information, deciding on a consultant pattern inhabitants is essential to keep away from sampling errors and make sure the accuracy of your outcomes. A consultant pattern is one which precisely displays the inhabitants’s traits, behaviors, and attitudes.
Choosing a Consultant Pattern Inhabitants
To pick a consultant pattern inhabitants, you must observe these pointers:
-
Outline your goal inhabitants and the sampling body, which is the listing of people or objects from which your pattern will probably be drawn.
For instance, in the event you’re finding out the voting habits of a selected area, your sampling body may embrace all registered voters in that area. -
Make sure that your pattern is randomly chosen from the sampling body to attenuate bias and be certain that every particular person or merchandise has an equal likelihood of being chosen.
You need to use methods like random quantity era or stratified sampling to realize this. -
Think about the scale and demographics of your pattern to make sure that it precisely displays the inhabitants’s traits.
For instance, in the event you’re finding out the opinions of adults aged 18-64, your pattern ought to embrace a mixture of individuals from completely different age teams, genders, ethnicities, and socio-economic backgrounds.
By following these pointers, you’ll be able to choose a pattern inhabitants that precisely represents the inhabitants and reduces the danger of sampling errors.
Significance of Pattern Dimension and Figuring out an Sufficient Pattern Dimension
The pattern dimension is the variety of people or objects in your pattern, and it performs a essential function in figuring out the accuracy of your outcomes. A big pattern dimension sometimes gives extra correct outcomes than a small pattern dimension, but it surely additionally will increase the price and time required to gather and analyze the info. Listed below are some components to contemplate when figuring out an enough pattern dimension:
-
The margin of error, which is the utmost distinction between the pattern’s estimate and the true inhabitants parameter.
A smaller margin of error sometimes requires a bigger pattern dimension. -
The boldness degree, which is the probability that the pattern’s estimate falls inside a sure vary of the true inhabitants parameter.
The next confidence degree sometimes requires a bigger pattern dimension. -
The variability of the inhabitants, which may be measured utilizing statistics like customary deviation or variance.
Populations with excessive variability sometimes require bigger pattern sizes.
You need to use formulation just like the Cochran components or the Kish components to estimate the required pattern dimension primarily based on these components.
Methods for Lowering Pattern Bias, What are one of the best methods to forestall a sampling error
Sampling bias happens when the pattern is chosen in a manner that systematically deviates from the inhabitants’s traits, resulting in inaccurate outcomes. Listed below are some methods to cut back pattern bias:
-
Use stratified sampling, which entails dividing the inhabitants into subgroups (strata) and deciding on a random pattern from every stratum.
This helps to make sure that the pattern represents the inhabitants’s traits and reduces the danger of sampling bias. -
Use random sampling from the sampling body, as talked about earlier.
This ensures that every particular person or merchandise has an equal likelihood of being chosen and reduces the danger of sampling bias. -
Use weighting or calibration methods to regulate the pattern’s traits to match the inhabitants’s traits.
For instance, in case your pattern overrepresents a selected demographic group, you need to use weighting methods to regulate the pattern to match the inhabitants’s demographics.
By utilizing these methods, you’ll be able to cut back pattern bias and improve the accuracy of your outcomes.
Guaranteeing Pattern Range
Pattern range refers back to the diploma to which the pattern represents the inhabitants’s traits, behaviors, and attitudes. Listed below are some strategies to make sure pattern range:
- Use stratified sampling, as talked about earlier, to make sure that the pattern represents the inhabitants’s subgroups.
- Use random sampling from the sampling body to make sure that every particular person or merchandise has an equal likelihood of being chosen and reduces the danger of sampling bias.
-
Use weighting or calibration methods to regulate the pattern’s traits to match the inhabitants’s traits.
For instance, in case your pattern overrepresents a selected demographic group, you need to use weighting methods to regulate the pattern to match the inhabitants’s demographics.
By following these strategies, you’ll be able to be certain that your pattern is numerous and precisely represents the inhabitants’s traits, behaviors, and attitudes.
Amassing Correct Information: What Are The Greatest Methods To Stop A Sampling Error
Amassing correct information is a vital step in minimizing sampling error. Information assortment errors can come up from numerous sources, together with human bias, incomplete or lacking information, and defective measurement instruments. To make sure the accuracy of collected information, researchers should implement efficient methods to attenuate errors and validate collected information.
When accumulating information, it is important to pay attention to the potential biases that may have an effect on information accuracy. These biases can stem from numerous sources, together with the researcher’s personal assumptions and experiences.
Information Validation Methods
Information validation is a essential step in making certain the accuracy of collected information. It entails checking the info for errors and inconsistencies, in addition to verifying its completeness and accuracy. A number of information validation methods may be employed, together with:
- Vary checking: This entails verifying that information factors fall inside a specified vary.
- Format checking: This entails verifying that information factors conform to a specified format, similar to a date or time.
- Logical checking: This entails verifying that information factors fulfill sure logical situations, similar to checking for inconsistencies in a dataset.
Information validation may be carried out manually or utilizing automated instruments, relying on the scale and complexity of the dataset.
Frequent Information Assortment Strategies and their Potential Biases
A number of information assortment strategies can be utilized, every with its personal set of potential biases.
-
Surveys
: Surveys may be susceptible to bias from non-response, the place contributors don’t reply to the survey, or from non-coverage, the place sure populations are excluded from the survey.
-
Interviews
: Interviews may be susceptible to bias from the researchers’ personal assumptions and experiences, in addition to from the contributors’ need to current themselves in a optimistic mild.
-
On-line information assortment
: On-line information assortment may be susceptible to bias from self-selection, the place contributors select to take part primarily based on their very own pursuits or demographics.
It is important to pay attention to these potential biases and to take steps to mitigate them, similar to utilizing random sampling, implementing information validation methods, and minimizing the introduction of researcher bias.
The Function of Information Processing in Lowering Sampling Error
Information processing entails cleansing, reworking, and analyzing the collected information. This step can play a essential function in decreasing sampling error by figuring out and correcting errors, dealing with lacking information, and deciding on probably the most applicable statistical strategies for information evaluation.
- Information cleansing: This entails figuring out and correcting errors within the information, similar to typos or inconsistencies.
- Information transformation: This entails changing the info right into a format that’s appropriate for evaluation, similar to changing dates or instances right into a numerical format.
- Information evaluation: This entails deciding on statistical strategies which can be most suited to the info and the analysis query, and decoding the outcomes of the evaluation.
Efficient information processing may help to cut back sampling error by figuring out and correcting errors, dealing with lacking information, and deciding on probably the most applicable statistical strategies for information evaluation.
Information Assortment Strategies and their Potential Biases
A number of information assortment strategies can be utilized, every with its personal set of potential biases.
Instance of Information Assortment utilizing Surveys
Surveys could be a helpful information assortment technique, however they aren’t with out their potential biases. One instance of a survey is the US Census Bureau’s American Group Survey (ACS). The ACS is a self-administered survey that collects information on the demographics and socioeconomic traits of the US inhabitants.
American Group Survey
,
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing | Details about housing traits, similar to sort of housing, age of housing, and lease |
| Schooling | Details about instructional attainment, similar to degree of training and years of education |
The ACS is obtainable in a number of languages and is designed to gather information from a consultant pattern of the US inhabitants. Nevertheless, the survey has been criticized for its potential biases, similar to non-response and non-coverage.
Instance of Information Assortment utilizing Interviews
Interviews could be a helpful information assortment technique, however they aren’t with out their potential biases. One instance of an interview is the Pew Analysis Heart’s phone interviews with adults in the USA.
Pew Analysis Heart
,
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Demographics | Details about respondents’ demographics, similar to age, intercourse, and revenue |
| Opinions | Details about respondents’ opinions on a variety of matters, similar to politics and social points |
The Pew Analysis Heart’s phone surveys are designed to gather information from a consultant pattern of adults in the USA. Nevertheless, the survey has been criticized for its potential biases, similar to interviewer bias and respondent bias.
Deciphering Information with Confidence
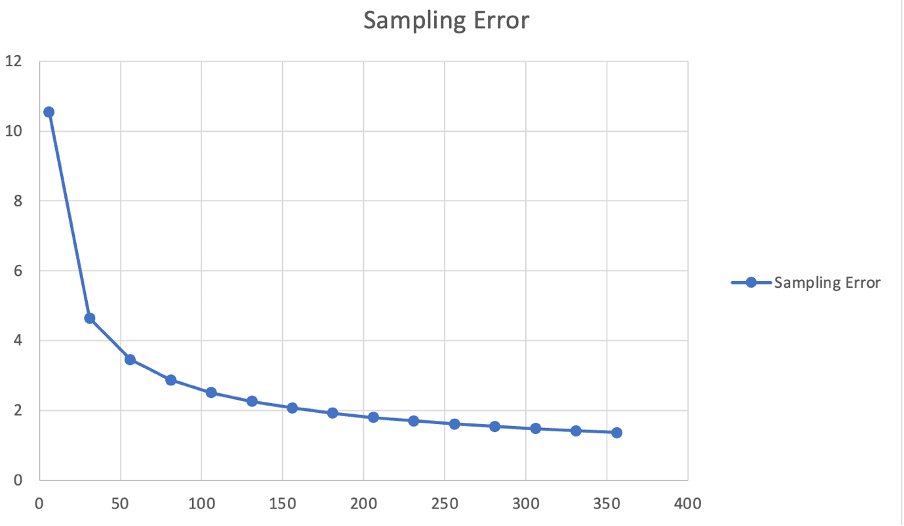
Analyzing information is a vital step in figuring out patterns, relationships, and traits. Nevertheless, it is equally vital to validate the accuracy and completeness of the info to keep away from sampling errors. By decoding information with confidence intervals, researchers can gauge the reliability of their findings and make knowledgeable selections.
Statistical Strategies for Detecting Sampling Error
Statistical strategies present a framework for detecting sampling errors and correcting biases. Some widespread methods embrace:
- The Legislation of Massive Numbers (LLN): This precept means that because the pattern dimension will increase, the noticed frequencies or averages will converge to their true inhabitants means.
- The Central Restrict Theorem (CLT): This theorem states that the sampling distribution of a statistic (just like the imply or proportion) will probably be roughly regular, even when the underlying inhabitants distribution isn’t regular.
- Speculation Testing: This entails testing a null speculation that there isn’t a distinction or relationship between variables, and accepting or rejecting the speculation primarily based on the check outcomes.
Statistical strategies provide a scientific and dependable strategy to information evaluation, enabling researchers to determine and quantify sampling errors.
Validating Information and Figuring out Outliers
Validating information is a essential step in making certain the accuracy and completeness of the info. Figuring out outliers, lacking values, or inconsistent information factors can present worthwhile insights into the info high quality and sampling course of. Some widespread methods for validating information embrace:
- Visible Inspection: Plotting the info on a graph or chart may help determine uncommon patterns or traits which will point out sampling errors.
- Statistical Checks: Utilizing statistical assessments, such because the Shapiro-Wilk check or the Kolmogorov-Smirnov check, may help decide if the info follows a particular distribution or reveals irregular conduct.
- Information Cleansing: Manually inspecting and correcting information entries, dealing with lacking values, and updating information codecs may help guarantee information accuracy and consistency.
Invalidating information requires a scientific and thorough strategy to make sure that the outcomes are dependable and correct.
Developing and Deciphering Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals present a variety of values inside which the true inhabitants parameter is more likely to lie. By establishing and decoding confidence intervals, researchers can quantify the uncertainty related to their estimates. Some key points of confidence intervals embrace:
- Confidence Degree: The boldness degree represents the proportion of the time when the interval would comprise the true parameter worth. Frequent confidence ranges embrace 90%, 95%, or 99%.
- Margin of Error: The margin of error represents the utmost quantity of error that may be current within the estimate. This worth is immediately associated to the arrogance degree and pattern dimension.
- Interval Width: The width of the interval represents the vary of values inside which the true parameter is more likely to lie.
Confidence intervals present a robust device for researchers to specific the uncertainty related to their findings and make knowledgeable selections.
Contemplating Potential Biases in Information Evaluation
Biases can happen at numerous phases of the info assortment course of, from sampling to evaluation. Recognizing and addressing potential biases is essential to making sure the accuracy and reliability of the outcomes. Some widespread biases embrace:
| Biases | Description |
|---|---|
| Audit Bias | Audit bias happens when information is collected in a sequential method, resulting in variations within the information on account of variations within the pattern. |
| Attrition Bias | Attrition bias happens when information is collected at completely different time limits, resulting in variations within the information on account of adjustments within the pattern. |
| Measurement Bias | Measurement bias happens when the tactic of information assortment impacts the outcomes. |
Figuring out and addressing biases requires a radical understanding of the info assortment course of and the potential sources of error.
Greatest Practices for Sampling
In the case of sampling, accuracy is essential. A well-designed sampling technique can be certain that the outcomes are dependable and consultant of the inhabitants. On this part, we are going to talk about one of the best practices for choosing a pattern inhabitants and evaluate completely different sampling strategies.
Organizing the Sampling Body
The sampling body is the listing of items from which the pattern will probably be chosen. It is important to make sure that the sampling body is complete, up-to-date, and free from errors. This may be achieved by:
- Fastidiously reviewing and updating the sampling body
- Verifying the accuracy of the data
- Guaranteeing that the sampling body is consultant of the inhabitants
By organizing the sampling body successfully, you’ll be able to cut back errors and be certain that the pattern is consultant of the inhabitants.
Stratification
Stratification entails dividing the inhabitants into distinct subgroups, known as strata. This may be carried out primarily based on related traits similar to age, intercourse, or location. By sampling inside every stratum, you’ll be able to be certain that the pattern is consultant of the inhabitants and cut back bias.
Stratification helps to make sure that the pattern is consultant of the inhabitants by decreasing bias and rising precision.
Cluster Sampling
Cluster sampling entails dividing the inhabitants into clusters and sampling a random subset of those clusters. This may be an environment friendly solution to pattern massive populations, particularly when assets are restricted.
Cluster sampling may be an environment friendly solution to pattern massive populations, however it might end in biased samples if the clusters are usually not consultant of the inhabitants.
Random Sampling
Random sampling entails deciding on a random subset of items from the inhabitants. This may be carried out utilizing numerous methods, similar to easy random sampling or systematic random sampling.
Random sampling is a straightforward and efficient solution to choose a pattern, however it might end in unrepresentative samples if the items are usually not randomly chosen.
Documenting Sampling Procedures
It is important to doc the sampling procedures, together with the strategies used, the sampling body, and the pattern dimension. This may help be certain that the sampling course of is clear and reproducible.
Documenting sampling procedures is important to make sure that the sampling course of is clear and reproducible.
| Technique | Description | Benefits | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random | Every unit has an equal likelihood of being chosen. | Easy to implement, low bias | Could end in unrepresentative samples |
| Stratified | Sampling is completed inside distinct teams. | Reduces bias, ensures illustration | Might be time-consuming and costly |
| Cluster | Sampling is completed inside clusters of items. | Reduces journey prices, will increase effectivity | Could end in biased samples if clusters are usually not consultant |
Evaluating Sampling Strategies
Evaluating completely different sampling strategies is essential in understanding the implications of every technique on sampling error. Sampling strategies may be labeled into two most important classes: sampling with substitute and sampling with out substitute.
Sampling with substitute entails deciding on a pattern from the inhabitants the place the chosen objects are positioned again into the inhabitants earlier than the subsequent choice. This course of continues till the required pattern dimension is achieved. Then again, sampling with out substitute entails deciding on a pattern from the inhabitants the place the chosen objects are usually not positioned again into the inhabitants. This technique is usually utilized in many fields, together with statistics, economics, and social sciences.
Variations Between Sampling With and With out Substitute
- Sampling With Substitute is often utilized in conditions the place the inhabitants is massive and it is doable to make a number of attracts with out depleting the inhabitants. This technique can also be used when the pattern dimension is a small fraction of the inhabitants. Examples of such conditions embrace random sampling from a producing course of or from a big buyer base.
- Sampling With out Substitute is often utilized in conditions the place the inhabitants is small or when it isn’t doable to make a number of attracts with out depleting the inhabitants. This technique can also be utilized in conditions the place the inhabitants is heterogeneous and the pattern dimension is a major fraction of the inhabitants.
This distinction is vital as a result of the tactic used can considerably impression the accuracy of the pattern and the outcomes obtained from the evaluation.
Implications of Every Technique on Sampling Error
| Technique | Sampling Error |
|---|---|
| Sampling With Substitute | The sampling error is often smaller as a result of the inhabitants isn’t depleted. |
| Sampling With out Substitute | The sampling error is often bigger as a result of the inhabitants is depleted, and the pattern dimension is a major fraction of the inhabitants. |
The selection of sampling technique finally will depend on the precise analysis questions and the assets obtainable. Researchers should rigorously think about the trade-offs between sampling error and useful resource constraints.
Selecting the Proper Sampling Technique
Sampling With Substitute is often most popular when:
- The inhabitants is massive and it is doable to make a number of attracts with out depleting the inhabitants.
- The pattern dimension is a small fraction of the inhabitants.
Sampling With out Substitute is often most popular when:
- The inhabitants is small or when it isn’t doable to make a number of attracts with out depleting the inhabitants.
- The inhabitants is heterogeneous and the pattern dimension is a major fraction of the inhabitants.
When making a selection, researchers should think about the trade-offs between sampling error and useful resource constraints.
The selection of sampling technique ought to be primarily based on the precise analysis questions and the assets obtainable.
This ensures that the analysis design is rigorous and that the outcomes obtained from the evaluation are generalizable to the inhabitants.
Abstract

By following one of the best practices Artikeld on this dialogue, researchers can reduce the danger of sampling error and be certain that their findings are correct and dependable. Choosing a consultant pattern inhabitants, utilizing sturdy information assortment strategies, and analyzing information accurately are all essential steps in stopping sampling error and bettering the standard of analysis outcomes.
Skilled Solutions
What’s sampling error, and the way does it impression analysis outcomes?
Sampling error happens when there’s a distinction between the pattern information and the inhabitants information, which may occur on account of numerous causes similar to biased sampling, information assortment errors, or under- or over-sampling. This could result in inaccurate or deceptive outcomes, which may have important penalties in fields similar to medication, social sciences, or enterprise.
How can researchers choose a consultant pattern inhabitants?
Researchers can choose a consultant pattern inhabitants through the use of stratified sampling strategies, the place the inhabitants is split into distinct teams or strata, and a random pattern is taken from every stratum. This ensures that the pattern is consultant of the inhabitants and reduces the danger of biased sampling.
What are some widespread information assortment errors that may result in sampling error?
Frequent information assortment errors that may result in sampling error embrace measurement errors, response errors, and non-response errors. Measurement errors happen when the info collected is inaccurate or incomplete. Response errors happen when respondents present inaccurate or biased info. Non-response errors happen when sure people or teams are excluded from the survey on account of numerous causes similar to language limitations or refusal to take part.