Choose the macromolecule and reasoning that most closely fits the diagram. – Delving into the world of macromolecules, this text guides readers by way of a complete overview of their construction, properties, and capabilities. With the supplied diagram serving as a visible assist, learners will develop a deeper understanding of the intricacies of macromolecules and the way they work together with their atmosphere.
The parts of a macromolecule embrace monomers, polymers, branching, and cross-linking. A quick comparability of various kinds of macromolecules, together with carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, may also be lined. Moreover, this text explores the exterior elements that have an effect on macromolecule properties and behaviors, discussing temperature, pH, and the presence of solvents.
Macromolecule Diagram Overview: Choose The Macromolecule And Reasoning That Finest Suits The Diagram.
The macromolecule diagram is a visible illustration of the advanced construction of macromolecules, that are giant biomolecules composed of smaller models known as monomers. These diagrams present worthwhile insights into the properties and capabilities of macromolecules, akin to their measurement, form, and interactions with their atmosphere.
Parts of the Macromolecule Diagram
The parts of the macromolecule diagram may be summarized within the following desk:
| Part | Description |
|————|———————-|
| Monomers | Small models of a |
| | macromolecule |
| Polymers | Lengthy chains of |
| | monomers |
| Branching | Extension of the |
| | polymer chain |
| Cross-link | Junctions between |
| | polymer chains |
The parts of the macromolecule diagram play essential roles in figuring out its construction and properties. Monomers are the constructing blocks of macromolecules, whereas polymers are the lengthy chains shaped by the repetition of monomers. Branching happens when the polymer chain extends in several instructions, and cross-links are shaped when two or extra polymer chains are joined collectively.
Interactions with the Surroundings
Macromolecules work together with their atmosphere by way of varied mechanisms, together with:
- Hydrogen bonding: Macromolecules can kind hydrogen bonds with different molecules, which play a vital function of their interactions with water and different solvents.
- Electrostatic interactions: Macromolecules may work together by way of electrostatic forces, that are influenced by the charged teams current on their floor.
- Van der Waals interactions: Macromolecules can work together by way of van der Waals forces, which come up from the short-term dipoles current on their floor.
- Bonding and adsorption: Macromolecules may work together by way of bonding and adsorption, the place they kind covalent or ionic bonds with different molecules or surfaces.
These interactions play an important function in figuring out the habits and performance of macromolecules in several environments. For instance, the interactions between a macromolecule and a solvent can have an effect on its solubility, stability, and reactivity.
Construction and Perform
The construction and performance of macromolecules are carefully linked, and their interactions with their atmosphere play a vital function in figuring out their properties and behaviors. Understanding the macromolecule diagram and its parts is important for understanding the properties and capabilities of those advanced biomolecules.
Organic Implications
The research of macromolecules has important implications for our understanding of organic programs and processes. For instance, the construction and interactions of macromolecules play a vital function in figuring out the properties and capabilities of cells, tissues, and organs. Understanding these interactions will help us develop new remedies and therapies for a variety of illnesses and problems.
Macromolecule Sorts and Their Traits

Within the realm of biology, macromolecules are important constructing blocks of cells that carry out varied capabilities. They’re shaped by the polymerization of smaller molecular models, leading to advanced constructions with distinctive properties.
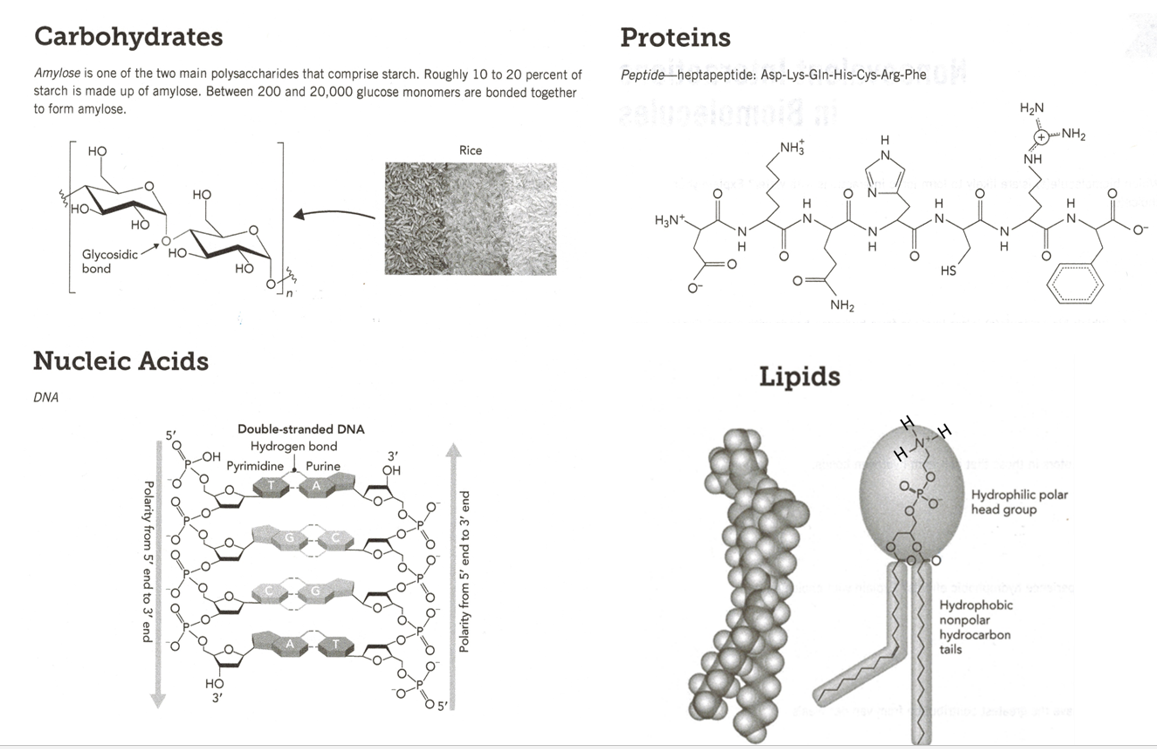
Macromolecules may be categorized into 4 most important sorts: carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Every kind has distinct traits and performs a vital function within the functioning of dwelling organisms.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They’re primarily concerned in vitality storage and structural assist. This numerous group of macromolecules consists of sugars, starch, and cellulose.
- Sugars function a major supply of vitality for cells, as they are often damaged down into glucose.
- Starch, a kind of polysaccharide, is saved in plant cells and serves as a backup vitality supply.
- Cellulose is a structural element of plant cell partitions, offering rigidity and assist.
Proteins
Proteins are advanced molecules composed of amino acids. They’re important for enzyme motion, transportation of vitamins, and varied different mobile processes.
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids, particularly DNA and RNA, are answerable for storing genetic info and facilitating cell development. This important operate permits the transmission of traits from one era to the following.
- DNA acts as a blueprint for the event of an organism, containing the directions for the synthesis of proteins.
- RNA performs an important function in protein synthesis, because it interprets the genetic info saved in DNA into the sequence of amino acids required for protein synthesis.
Lipids
Lipids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They primarily function vitality storage and structural parts of mobile membranes.
- Triglycerides are a kind of lipid that shops vitality, breaking down into fatty acids when wanted by the cell.
- Phospholipids are important parts of cell membranes, forming a bilayer construction that separates the cell’s inside from its atmosphere.
The distinctive construction of macromolecules, together with the association of their constituent components and bonding patterns, considerably influences their properties. For example, the presence of hydrophobic areas in lipids permits them to kind non-polar interactions, whereas carbohydrates are likely to have hydrophilic properties, enabling them to work together with water.
Understanding the properties and capabilities of macromolecules is essential in varied fields, akin to medication, agriculture, and biotechnology. This information has led to important developments within the growth of recent remedies, crop enchancment, and the manufacturing of biofuels.
Macromolecule Capabilities and Organic Roles

Macromolecules are the constructing blocks of life, enjoying essential roles in varied organic processes. Every kind of macromolecule has distinct capabilities and organic roles, making them important for sustaining life. On this part, we’ll discover the organic capabilities of various macromolecule sorts and their participation in organic processes.
Vitality Storage and Structural Help
Carbohydrates and lipids function vitality storage molecules, offering vitality for cells to operate correctly. In addition they assist cell construction by forming the exoskeletons of cells, akin to within the case of micro organism and archaea. Moreover, carbohydrates contribute to the structural assist of cells by forming glycoproteins and glycolipids that assist keep cell form.
| Macromolecule | Organic function |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Vitality storage and structural assist |
| Lipids | Vitality storage and structural assist |
Enzyme Motion and Structural Help
Proteins function enzymes, catalyzing chemical reactions that happen inside cells. In addition they play essential roles in structural assist by forming the cytoskeleton of cells, offering form and mechanical power. Proteins additionally kind receptors that bind to hormones and neurotransmitters, facilitating sign transduction.
| Macromolecule | Organic function |
|---|---|
| Proteins | Enzyme motion and structural assist |
Storage of Genetic Data and Replication
Nucleic acids, together with DNA and RNA, retailer and transmit genetic info. They’re answerable for the replication of cells, making certain that genetic info is handed from one era to the following.
| Macromolecule | Organic function |
|---|---|
| Nucleic acids | Storage of genetic info and replication |
Malfunction of Macromolecules and Illness
Malfunction of macromolecules can result in varied illnesses, together with genetic problems, metabolic problems, and structural problems. For instance, mutations in DNA can result in genetic problems, whereas defects in enzymes can lead to metabolic problems. Equally, defects in structural proteins can result in muscular dystrophy.
Mutation in a single gene could cause a genetic dysfunction.
Macromolecule Interactions and Associations
Macromolecules, akin to DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, work together with one another and their atmosphere by way of varied chemical and bodily forces. These interactions are essential for sustaining the construction and performance of dwelling organisms, facilitating advanced organic processes, and permitting cells to adapt to altering environments.
Interactions between Macromolecules
Macromolecules work together with one another by way of weak bonds, akin to hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and ionic bonds. These interactions play a vital function in sustaining the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary constructions of proteins, in addition to the helical construction of DNA. Moreover, macromolecules can kind complexes with one another, such because the protein-nucleic acid complexes concerned in gene regulation.
- Hydrogen Bonds: Weak bonds between electronegative atoms, akin to oxygen and nitrogen, that play a vital function in sustaining the construction of RNA and DNA.
- Hydrophobic Interactions: Engaging forces between non-polar molecules that drive the formation of protein constructions and the affiliation of lipids in cell membranes.
- Ionic Bonds: Electrostatic points of interest between positively and negatively charged ions which are necessary in protein-ligand interactions and the binding of ions to nucleic acids.
The precise interactions between macromolecules depend upon the chemical composition and structural properties of the molecules concerned. Understanding these interactions is important for predicting the habits of organic programs and growing new therapies for illnesses related to protein misfolding or nucleic acid dysfunction.
Macromolecule Associations with the Surroundings
Macromolecules work together with the atmosphere by way of varied chemical and bodily forces, akin to ionic interactions, hydrogen bonding, and Van der Waals forces. These interactions are essential for sustaining the construction and performance of dwelling organisms, facilitating advanced organic processes, and permitting cells to adapt to altering environments.
Water, as a solvent, performs a vital function in macromolecule interactions and associations by mediating ionic interactions, hydrophobic interactions, and hydrogen bonding.
Function of Macromolecules in Mobile Processes, Choose the macromolecule and reasoning that most closely fits the diagram.
Macromolecules take part in advanced organic processes, akin to protein folding and transport, by way of particular interactions with different macromolecules and the atmosphere. These processes are important for sustaining mobile homeostasis and regulating the expression of genes.
Protein folding and transport contain a sequence of interactions between proteins, akin to chaperones and transport proteins, and the atmosphere. This course of is essential for sustaining protein construction and performance, in addition to regulating gene expression.
Evaluating the Construction and Properties of Completely different Macromolecules
Macromolecules exhibit distinct structural and useful properties that depend upon the chemical composition and sequence of their constituent monomers. Understanding the construction and properties of macromolecules is important for predicting their habits in organic programs and growing new therapies for illnesses related to protein dysfunction or nucleic acid malfunction.
- Polysaccharides: Advanced carbohydrates composed of a number of monosaccharide models that play a essential function in vitality storage, cell signaling, and construction.
- Proteins: Polymers composed of amino acids that carry out a variety of organic capabilities, together with enzyme catalysis, structural assist, and cell signaling.
- Nucleic Acids: Polymers composed of nucleotides that retailer genetic info and regulate gene expression by way of particular interactions with proteins.
The precise properties of macromolecules depend upon their chemical composition, sequence, and construction. Understanding the construction and properties of macromolecules is important for predicting their habits in organic programs and growing new therapies for illnesses related to protein dysfunction or nucleic acid malfunction.
Ending Remarks
By navigating by way of the varied facets of macromolecules, together with their construction, properties, and capabilities, readers will achieve a profound understanding of those advanced organic molecules and their very important roles throughout the human physique. Understanding the interactions and associations between macromolecules is essential for greedy the intricacies of organic processes, making this text a useful useful resource for each college students and professionals alike.
FAQ Information
Q: What’s the major operate of macromolecules in dwelling organisms?
A: Macromolecules function important constructing blocks of dwelling organisms, offering structural assist, vitality storage, and taking part in varied organic processes, akin to enzyme motion and transportation of vitamins.
Q: How do exterior elements, akin to temperature and pH, have an effect on macromolecule properties and behaviors?
A: Exterior elements like temperature and pH could cause denaturation or unfolding of macromolecules, resulting in modifications of their construction and performance. The presence of solvents may affect macromolecule solubility, influencing their habits.
Q: What are some widespread sorts of macromolecules and their respective capabilities?
A: Carbohydrates retailer vitality and supply structural assist, whereas proteins carry out varied capabilities, together with enzyme motion and transportation of vitamins. Nucleic acids retailer genetic info and take part in replication, and lipids function vitality storage models and supply structural assist.