Which regression equation most closely fits these information – As regression evaluation is a vital step in information modeling, deciding on the appropriate regression equation for a given dataset is an important job. In numerous domains equivalent to finance, social sciences, and engineering, regression equations play an important function in figuring out patterns and relationships between variables.
This text goals to offer an in-depth understanding of regression equations and their functions, together with the frequent sorts, choose the perfect one, and methods for evaluating their goodness of match.
Forms of Regression Equations
Regression equations are extensively used statistical evaluation methods to ascertain relationships between variables, predict outcomes, and determine patterns in information. The selection of regression equation is dependent upon the character of the info, the connection between the variables, and the analysis query being addressed. On this part, we are going to talk about 4 frequent forms of regression equations: linear, logistic, polynomial, and non-linear regression equations.
Variations and Comparability of Linear, Logistic, Polynomial, and Non-Linear Regression Equations
Linear regression equations are used when the connection between the dependent variable and unbiased variable will be expressed as a straight line. Logistic regression equations are used when the dependent variable is a binary (0/1) variable. Polynomial regression equations are used when the connection between the dependent variable and unbiased variable is non-linear and will be expressed as a polynomial operate. Non-linear regression equations are used when the connection between the dependent variable and unbiased variable is complicated and non-linear.
- Linear Regression Equations
- Logistic Regression Equations
- Polynomial Regression Equations
- Non-Linear Regression Equations
The linear regression equation is probably the most generally used regression equation. It’s used when the connection between the dependent variable and unbiased variable will be expressed as a straight line. The linear regression equation will be expressed as:
y = β0 + β1x + ε
The place y is the dependent variable, x is the unbiased variable, β0 is the intercept, β1 is the slope coefficient, and ε is the error time period.
Logistic regression equations are used when the dependent variable is a binary (0/1) variable. The logistic regression equation will be expressed as:
log( p / (1-p) ) = β0 + β1x + ε
The place p is the likelihood of the dependent variable being 1, x is the unbiased variable, β0 is the intercept, β1 is the slope coefficient, and ε is the error time period.
Polynomial regression equations are used when the connection between the dependent variable and unbiased variable is non-linear and will be expressed as a polynomial operate. The polynomial regression equation will be expressed as:
y = β0 + β1x + β2x^2 + … + βnx^n + ε
The place y is the dependent variable, x is the unbiased variable, β0 is the intercept, β1 is the slope coefficient, β2 is the quadratic coefficient, and ε is the error time period.
Non-linear regression equations are used when the connection between the dependent variable and unbiased variable is complicated and non-linear. The non-linear regression equation will be expressed as:
y = f(x, β0, β1, …, βn) + ε
The place y is the dependent variable, x is the unbiased variable, β0 is the intercept, β1 is the slope coefficient, β2 is the quadratic coefficient, and ε is the error time period.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Every Sort of Regression Equation
| Equation Sort | Benefits | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression Equation | Simple to interpret and perceive, extensively relevant | Not appropriate for non-linear relationships |
| Logistic Regression Equation | Appropriate for binary dependent variables, straightforward to interpret | Not appropriate for non-binary dependent variables, restricted to logistic operate |
| Polynomial Regression Equation | Appropriate for non-linear relationships, straightforward to interpret | Not appropriate for complicated relationships, could endure from overfitting |
| Non-Linear Regression Equation | Appropriate for complicated relationships, extensively relevant | Troublesome to interpret and perceive, could endure from overfitting |
Situations Underneath Which Every Sort of Regression Equation is Used
Linear regression equations are used when the connection between the dependent variable and unbiased variable will be expressed as a straight line. Logistic regression equations are used when the dependent variable is a binary (0/1) variable. Polynomial regression equations are used when the connection between the dependent variable and unbiased variable is non-linear and will be expressed as a polynomial operate. Non-linear regression equations are used when the connection between the dependent variable and unbiased variable is complicated and non-linear.
In abstract, the selection of regression equation is dependent upon the character of the info, the connection between the variables, and the analysis query being addressed. Every sort of regression equation has its personal benefits and drawbacks, and is utilized in totally different circumstances.
Choosing the Acceptable Regression Equation
Choosing the suitable regression equation is a vital step in statistical modeling. It entails figuring out the best-fitting mannequin that describes the connection between the unbiased and dependent variables. The chosen equation can have vital implications on the accuracy of predictions and the insights gained from the evaluation.
Components to Contemplate When Choosing a Regression Equation
When deciding on a regression equation, a number of elements should be considered. These embody:
Knowledge Distribution:
The distribution of the info is a vital consider deciding on the suitable regression equation. As an illustration, if the info is generally distributed, a linear regression mannequin could also be a good selection. Nonetheless, if the info is skewed, a change of the dependent variable could also be crucial to realize normality.
Relationship between Variables:
The connection between the unbiased and dependent variables is one other vital issue. If the connection is nonlinear, a linear regression mannequin might not be the only option. In such instances, a polynomial or logarithmic regression mannequin could also be extra appropriate.
Variety of Observations:
The variety of observations can be an necessary consideration. If the pattern dimension is small, an easier mannequin with fewer parameters could also be simpler. Nonetheless, if the pattern dimension is giant, a extra complicated mannequin with extra parameters could present a greater match.
Utilizing Residual Plots to Decide the Greatest Regression Equation
Residual plots are a useful gizmo for assessing the match of a regression equation. By inspecting the residuals, researchers can determine patterns or outliers which will point out a poor match. The next are some frequent points that may be recognized utilizing residual plots:
- Non-random patterns:
- Outliers:
- Heteroscedasticity:
* If the residuals exhibit a non-random sample, it might point out a poor match of the mannequin. As an illustration, if the residuals are positively or negatively correlated with the unbiased variable, it might recommend a non-linear relationship.
* Outliers can considerably affect the match of a regression equation. If a small variety of information factors are driving the mannequin’s predictions, they might not precisely replicate the connection between the variables. The outliers ought to be checked for accuracy and validity.
* If the variance of the residuals will increase with the unbiased variable, it might point out heteroscedasticity. In such instances, a weighted least squares mannequin could also be extra appropriate.
Utilizing Statistical Exams to Choose the Greatest Regression Equation
Statistical checks such because the F-test and R-squared can be utilized to guage the match of a regression equation. The next are some frequent checks used to pick out the perfect regression equation:
- F-test:
- R-squared:
* The F-test is used to evaluate the importance of the regression equation. If the F-statistic is excessive and the p-value is low, it means that the mannequin is an effective match.
* The R-squared worth measures the proportion of variance within the dependent variable that’s defined by the unbiased variable. A excessive R-squared worth signifies a very good match of the mannequin.
In conclusion, deciding on the suitable regression equation requires cautious consideration of a number of elements, together with information distribution, relationship between variables, and variety of observations. By utilizing residual plots and statistical checks, researchers can decide the perfect regression equation that precisely describes the connection between the variables.
“The very best regression equation is the one that gives probably the most correct predictions and insights into the connection between the variables.”
Widespread Regression Equations
Regression equations are mathematical fashions which can be used to ascertain a relationship between a number of unbiased variables and one dependent variable. On this part, we are going to discover three frequent forms of regression equations: easy linear regression, a number of linear regression, and logistic regression.
Easy Linear Regression
Easy linear regression is a kind of regression equation that entails one unbiased variable and one dependent variable. The equation for easy linear regression is given by:
[blockquote]
y = β0 + β1x + ε
[/blockquote]
the place y is the dependent variable, x is the unbiased variable, β0 is the intercept, β1 is the slope, and ε is the error time period.
Easy linear regression can be utilized to mannequin a variety of relationships, together with the connection between the value of a home and the variety of bedrooms it has, or the connection between the quantity of water utilized in a family and the variety of individuals dwelling within the family.
A number of Linear Regression
A number of linear regression is a kind of regression equation that entails a number of unbiased variables and one dependent variable. The equation for a number of linear regression is given by:
[blockquote]
y = β0 + β1×1 + β2×2 + … + βNxN + ε
[/blockquote]
the place y is the dependent variable, x1, x2, …, xN are the unbiased variables, β0 is the intercept, β1, β2, …, βN are the coefficients, and ε is the error time period.
A number of linear regression can be utilized to mannequin complicated relationships between a number of unbiased variables and one dependent variable. For instance, it may be used to mannequin the connection between the value of a automobile and a number of unbiased variables such because the variety of seats, the dimensions of the engine, and the kind of transmission.
Logistic Regression
Logistic regression is a kind of regression equation that’s used to mannequin binary outcomes, equivalent to 0/1 or sure/no. The equation for logistic regression is given by:
[blockquote]
p = 1 / (1 + e^(-z))
[/blockquote]
the place p is the likelihood of the end result, e is the bottom of the pure logarithm, and z is the linear predictor.
Logistic regression can be utilized to mannequin a variety of binary outcomes, together with the likelihood of a buyer shopping for a product primarily based on their demographic traits, or the likelihood of a affected person responding to a remedy primarily based on their medical historical past.
-
Logistic regression is extensively utilized in many fields, together with advertising, finance, and medication.
It may be used to mannequin complicated relationships between a number of unbiased variables and a binary final result.
For instance, it may be used to mannequin the likelihood of a buyer shopping for a product primarily based on their demographic traits, equivalent to age, earnings, and schooling stage. -
Logistic regression can be used to mannequin the likelihood of a affected person responding to a remedy primarily based on their medical historical past, equivalent to age, intercourse, and medical circumstances.
It can be used to mannequin the likelihood of an organization going bankrupt primarily based on its monetary metrics, equivalent to income, bills, and debt-to-equity ratio.
| Sort of Regression | Description | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Easy Linear Regression | Fashions a relationship between one unbiased variable and one dependent variable | y = β0 + β1x + ε |
| A number of Linear Regression | Fashions a relationship between a number of unbiased variables and one dependent variable | y = β0 + β1×1 + β2×2 + … + βNxN + ε |
| Logistic Regression | Fashions a binary final result primarily based on a number of unbiased variables | p = 1 / (1 + e^(-z)) |
Strategies for Evaluating Regression Equations: Which Regression Equation Greatest Matches These Knowledge
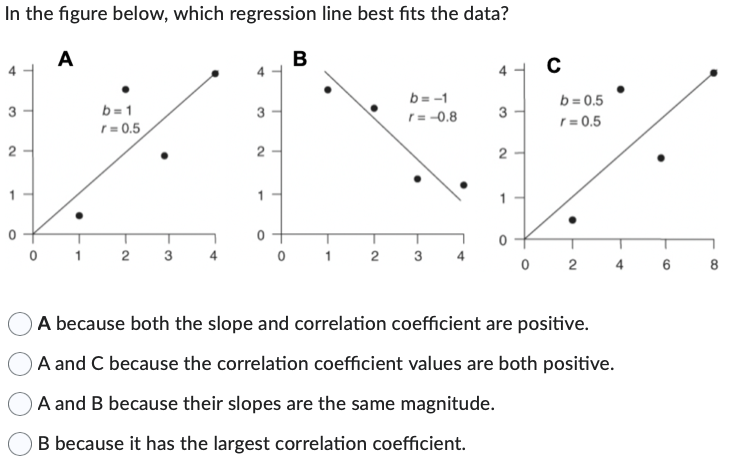
Evaluating the goodness of match of a regression equation is a vital step in guaranteeing that the mannequin precisely represents the underlying relationship between the unbiased variables and the dependent variable. A well-evaluated regression equation gives a dependable foundation for making predictions and understanding the relationships between variables.
Metrics for Evaluating Regression Equations
There are a number of metrics that can be utilized to guage the goodness of match of a regression equation, together with R-squared, imply squared error, and Akaike data criterion.
R-squared
R-squared, often known as the coefficient of willpower, measures the proportion of the variation within the dependent variable that’s defined by the unbiased variables. A excessive R-squared worth signifies a powerful relationship between the variables, whereas a low worth means that the mannequin doesn’t clarify a good portion of the variation within the dependent variable.
R-squared = 1 – (sum of squared residuals / complete sum of squares)
Imply Squared Error (MSE)
Imply squared error measures the common distinction between the noticed values and the expected values. It gives a sign of the accuracy of the mannequin in making predictions. A decrease MSE worth signifies a extra correct mannequin.
MSE = (sum of squared residuals) / (variety of observations – variety of unbiased variables)
Akaike Data Criterion (AIC)
AIC is a measure of the relative high quality of a mannequin by evaluating it to different fashions. A decrease AIC worth signifies a better-fitting mannequin.
AIC = 2k – 2ln(L)
the place ok is the variety of parameters within the mannequin and L is the utmost chance estimate of the mannequin.
Visualizing Regression Outcomes
Along with utilizing metrics to guage the goodness of match of a regression equation, it is usually necessary to visualise the outcomes of regression evaluation utilizing plots and tables. This will help to determine any patterns or outliers which may be current within the information.
- Scatter plots can be utilized to visualise the connection between the unbiased variables and the dependent variable.
- Error plots can be utilized to visualise the residuals of the mannequin, offering a sign of the accuracy of the mannequin.
- Residual plots can be utilized to determine any patterns or constructions within the residuals, indicating potential points with the mannequin.
These plots and tables can present a extra complete understanding of the relationships between the variables and will help to determine any points with the mannequin.
Widespread Challenges in Regression Evaluation

Regression evaluation is a strong statistical method for modeling the connection between a dependent variable and a number of unbiased variables. Nonetheless, it’s not resistant to challenges that may come up in the course of the information evaluation course of. On this part, we are going to talk about some frequent challenges that may have an effect on the accuracy and reliability of regression evaluation.
Concern of Multicollinearity
Multicollinearity happens when two or extra unbiased variables in a regression mannequin are extremely correlated with one another. This could trigger the estimates of the regression coefficients to be unstable and unreliable. Multicollinearity can result in a excessive diploma of variance inflation, leading to coefficients which can be extremely delicate to the presence of outliers and excessive values within the information. It’s usually indicated by a excessive worth of the variance inflation issue (VIF), which is a statistical measure of the extent to which a selected unbiased variable is correlated with different unbiased variables within the mannequin.
To evaluate multicollinearity, you may calculate the VIF for every unbiased variable within the mannequin. A VIF worth larger than 5 or 10 signifies the presence of multicollinearity. There are a number of methods for dealing with multicollinearity, together with:
- Eradicating a number of of the correlated unbiased variables from the mannequin. This will help to cut back the VIF and make the mannequin extra secure.
- Utilizing dimensionality discount methods, equivalent to principal part evaluation (PCA) or function choice. This will help to determine a very powerful options within the information and scale back the chance of multicollinearity.
- Utilizing regularization methods, equivalent to ridge regression or the Lasso. This will help to cut back the affect of multicollinearity on the estimates of the regression coefficients.
Dealing with Lacking Values in a Dataset
Lacking values can come up in a dataset for a wide range of causes, together with non-response, tools failure, or information entry errors. Lacking values can have a major affect on the accuracy and reliability of regression evaluation, as they’ll bias the estimates of the regression coefficients and result in incorrect conclusions. There are a number of methods for dealing with lacking values, together with:
- Ignoring the lacking values and continuing with the evaluation. This may be problematic if the lacking values aren’t lacking utterly at random (MCAR), as it will probably result in biased estimates of the regression coefficients.
- Utilizing imputation strategies, equivalent to imply or median imputation, to fill within the lacking values. This may be problematic if the lacking values aren’t lacking at random (MNAR), as it will probably result in biased estimates of the regression coefficients.
- Utilizing a number of imputation methods, equivalent to a number of imputation by chained equations (MICE). This will help to account for the uncertainty related to imputing lacking values and produce extra correct estimates of the regression coefficients.
Coping with Outliers in Regression Evaluation
Outliers can come up in a dataset for a wide range of causes, together with measurement errors, information entry errors, or unrepresentative observations. Outliers can have a major affect on the accuracy and reliability of regression evaluation, as they’ll bias the estimates of the regression coefficients and result in incorrect conclusions. There are a number of methods for coping with outliers, together with:
- Eradicating the outliers from the dataset. This may be problematic if the outliers aren’t merely errors, as they might include precious data that may assist to tell the evaluation.
- Remodeling the info, equivalent to by taking the logarithm or sq. root of the variables. This will help to cut back the affect of outliers on the estimates of the regression coefficients.
- Utilizing strong regression methods, equivalent to least absolute deviation or the Huber-White sandwich estimator. This will help to supply extra correct estimates of the regression coefficients by decreasing the affect of outliers.
Superior Regression Strategies
Superior regression methods are used to enhance the accuracy and robustness of regression fashions by addressing points equivalent to overfitting, multicollinearity, and non-linearity. These methods will be notably helpful when the info is complicated or when there are a number of variables that work together with one another.
Regularization in Regression Evaluation
Regularization is a technique used to stop overfitting in regression fashions. It does this by including a penalty time period to the loss operate, which discourages giant coefficients and makes the mannequin much less susceptible to overfitting. There are two most important forms of regularization: L1 and L2.
- L1 Regularization: The sort of regularization provides a time period to the loss operate that’s proportional to absolutely the worth of the coefficients. It units some coefficients to zero, successfully performing function choice.
- L2 Regularization: The sort of regularization provides a time period to the loss operate that’s proportional to the sq. of the coefficients. It doesn’t set coefficients to zero, however reasonably shrinks them in direction of zero, making the mannequin extra strong to noise.
Regularization will be utilized to the loss operate utilizing the next equation:
L = (1/n) * Σ (y_i – β_0 – β_1x_i1 – … – β_px_p)^2 + α * (|β_1| + |β_2| + … + |β_p|)
the place α is the regularization parameter, n is the variety of observations, β_i are the coefficients, x_ij are the predictor variables, and y_i are the response variables.
Motion Phrases in Regression Evaluation
Interplay phrases are used to mannequin the impact of a number of predictor variables on the response variable, with the impact relying on the extent of one other predictor variable. For instance, think about a examine of the impact of train and food regimen on physique weight, the place the impact of train is dependent upon the extent of food regimen.
body_weight = β_0 + β_1 * train + β_2 * food regimen + β_3 * train * food regimen
The time period train * food regimen represents the interplay between train and food regimen.
Machine Studying Algorithms for Regression Evaluation, Which regression equation most closely fits these information
Machine studying algorithms can be utilized to construct complicated regression fashions that seize non-linear relationships between variables. Two widespread algorithms for regression evaluation are resolution bushes and random forests.
Determination Tree:
A choice tree is a tree-like mannequin that splits the info into smaller subsets primarily based on the values of the predictor variables. Every node within the tree represents a choice rule, and the leaves symbolize the expected values.
Random Forest:
A random forest is an ensemble of a number of resolution bushes, educated on totally different subsets of the info. Every tree within the forest is educated on a unique subset of the info, and the expected values are mixed to supply the ultimate output.
Among the benefits of utilizing machine studying algorithms for regression evaluation embody their skill to deal with non-linear relationships, skill to deal with lacking information, and skill to deal with high-dimensional information.
Random Forest algorithm is especially helpful for regression evaluation, because it combines the predictions of a number of resolution bushes to attenuate overfitting, and it will probably deal with a lot of predictor variables.
-
Knowledge Preprocessing
– Dealing with lacking information
– Scaling and normalizing the info
– Function choice and engineering -
Mannequin Choice
– Choosing the proper algorithm (e.g., linear regression, resolution bushes, random forests)
-
Mannequin Analysis
– Assessing the efficiency of the mannequin utilizing metrics equivalent to imply squared error and R-squared
The usage of machine studying algorithms for regression evaluation can result in extra correct and strong fashions, particularly when in comparison with conventional linear regression fashions.
Abstract
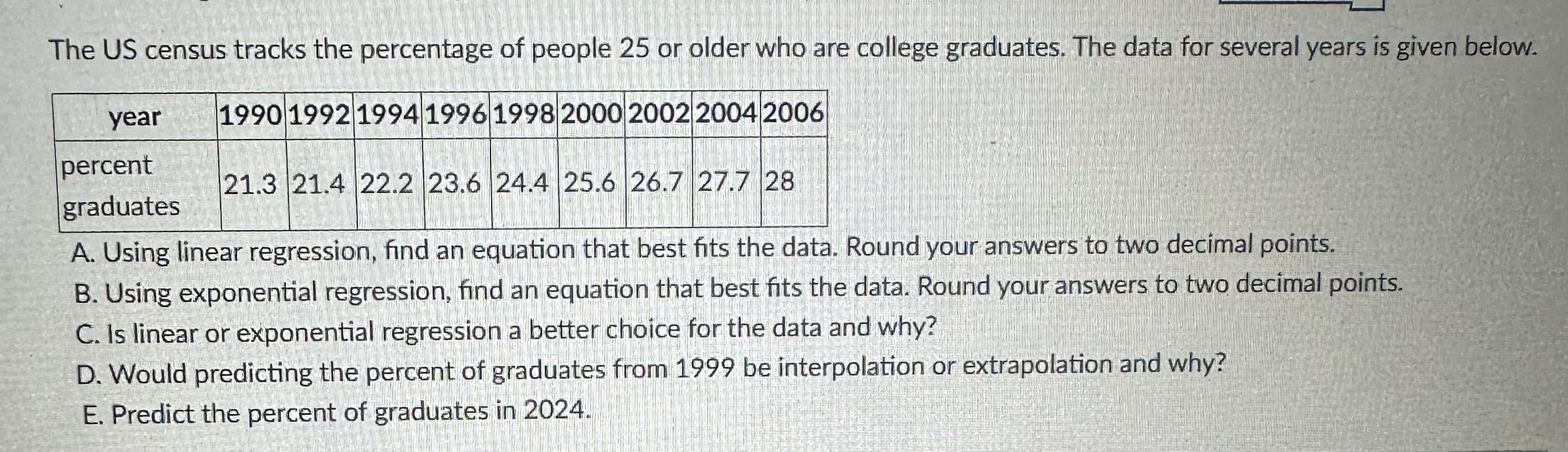
In conclusion, this text has offered a complete overview of regression equations and their significance in information modeling. By understanding the various kinds of regression equations, deciding on the appropriate one for a given dataset, and evaluating their goodness of match, researchers and practitioners can successfully make the most of regression evaluation to uncover precious insights and make knowledgeable choices.
Questions Usually Requested
What are the commonest forms of regression equations?
The commonest forms of regression equations embody linear, logistic, polynomial, and non-linear regression equations.
choose the perfect regression equation for a given dataset?
To pick out the perfect regression equation, think about elements equivalent to information distribution, relationship between variables, and variety of observations. Make the most of residual plots and statistical checks (e.g. F-test, R-squared) to find out the perfect regression equation.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of linear regression?
Linear regression is a extensively used regression equation. Its benefits embody simplicity, interpretability, and ease of implementation. Nonetheless, it assumes a linear relationship between variables, which can not all the time maintain.
consider the goodness of match of a regression equation?
To guage the goodness of match of a regression equation, use metrics equivalent to R-squared, imply squared error, and Akaike data criterion. Visualize the outcomes utilizing plots and tables.